- Philippines
-
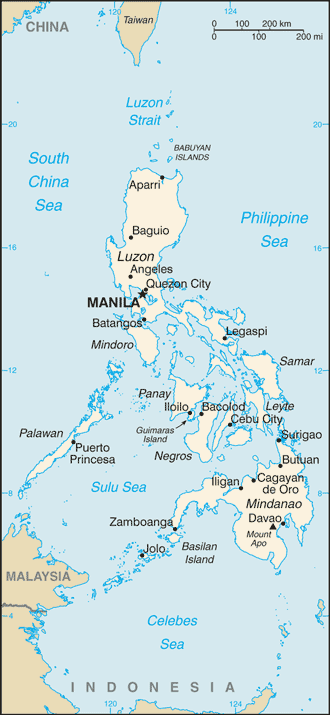 Introduction ::PhilippinesBackground:The Philippine Islands became a Spanish colony during the 16th century; they were ceded to the US in 1898 following the Spanish-American War. In 1935 the Philippines became a self-governing commonwealth. Manuel QUEZON was elected president and was tasked with preparing the country for independence after a 10-year transition. In 1942 the islands fell under Japanese occupation during World War II, and US forces and Filipinos fought together during 1944-45 to regain control. On 4 July 1946 the Republic of the Philippines attained its independence. A 20-year rule by Ferdinand MARCOS ended in 1986, when a ""people power"" movement in Manila (""EDSA 1"") forced him into exile and installed Corazon AQUINO as president. Her presidency was hampered by several coup attempts that prevented a return to full political stability and economic development. Fidel RAMOS was elected president in 1992. His administration was marked by increased stability and by progress on economic reforms. In 1992, the US closed its last military bases on the islands. Joseph ESTRADA was elected president in 1998. He was succeeded by his vice-president, Gloria MACAPAGAL-ARROYO, in January 2001 after ESTRADA's stormy impeachment trial on corruption charges broke down and another ""people power"" movement (""EDSA 2"") demanded his resignation. MACAPAGAL-ARROYO was elected to a six-year term as president in May 2004. Her presidency was marred by several corruption allegations but the Philippine economy was one of the few to avoid contraction following the 2008 global financial crisis, expanding each year of her administration. Benigno AQUINO III was elected to a six-year term as president in May 2010. The Philippine Government faces threats from several groups, some of which are on the US Government's Foreign Terrorist Organization list. Manila has waged a decades-long struggle against ethnic Moro insurgencies in the southern Philippines, which has led to a peace accord with the Moro National Liberation Front and ongoing peace talks with the Moro Islamic Liberation Front. The decades-long Maoist-inspired New People's Army insurgency also operates through much of the country. The Philippines faces increased tension with China over disputed territorial and maritime claims in the South China Sea.Geography ::PhilippinesLocation:Southeastern Asia, archipelago between the Philippine Sea and the South China Sea, east of VietnamGeographic coordinates:13 00 N, 122 00 EArea:total: 300,000 sq kmcountry comparison to the world: 73land: 298,170 sq kmwater: 1,830 sq kmArea - comparative:slightly larger than ArizonaLand boundaries:0 kmCoastline:36,289 kmMaritime claims:territorial sea: irregular polygon extending up to 100 nm from coastline as defined by 1898 treaty; since late 1970s has also claimed polygonal-shaped area in South China Sea up to 285 nm in breadthexclusive economic zone: 200 nmcontinental shelf: to depth of exploitationClimate:tropical marine; northeast monsoon (November to April); southwest monsoon (May to October)Terrain:mostly mountains with narrow to extensive coastal lowlandsElevation extremes:lowest point: Philippine Sea 0 mhighest point: Mount Apo 2,954 mNatural resources:timber, petroleum, nickel, cobalt, silver, gold, salt, copperLand use:arable land: 18%permanent crops: 17.33%other: 64.67% (2011)Irrigated land:18,790 sq km (2006)Total renewable water resources:479 cu km (2011)Freshwater withdrawal (domestic/industrial/agricultural):total: 81.56 cu km/yr (8%/10%/82%)per capita: 859.9 cu m/yr (2009)Natural hazards:astride typhoon belt, usually affected by 15 and struck by five to six cyclonic storms each year; landslides; active volcanoes; destructive earthquakes; tsunamisvolcanism: significant volcanic activity; Taal (elev. 311 m), which has shown recent unrest and may erupt in the near future, has been deemed a ""Decade Volcano"" by the International Association of Volcanology and Chemistry of the Earth's Interior, worthy of study due to its explosive history and close proximity to human populations; Mayon (elev. 2,462 m), the country's most active volcano, erupted in 2009 forcing over 33,000 to be evacuated; other historically active volcanoes include Biliran, Babuyan Claro, Bulusan, Camiguin, Camiguin de Babuyanes, Didicas, Iraya, Jolo, Kanlaon, Makaturing, Musuan, Parker, Pinatubo and RagangEnvironment - current issues:uncontrolled deforestation especially in watershed areas; soil erosion; air and water pollution in major urban centers; coral reef degradation; increasing pollution of coastal mangrove swamps that are important fish breeding groundsEnvironment - international agreements:party to: Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification, Endangered Species, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Marine Dumping, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Tropical Timber 83, Tropical Timber 94, Wetlands, Whalingsigned, but not ratified: Air Pollution-Persistent Organic PollutantsGeography - note:the Philippine archipelago is made up of 7,107 islands; favorably located in relation to many of Southeast Asia's main water bodies: the South China Sea, Philippine Sea, Sulu Sea, Celebes Sea, and Luzon StraitPeople and Society ::PhilippinesNationality:noun: Filipino(s)adjective: PhilippineEthnic groups:Tagalog 28.1%, Cebuano 13.1%, Ilocano 9%, Bisaya/Binisaya 7.6%, Hiligaynon Ilonggo 7.5%, Bikol 6%, Waray 3.4%, other 25.3% (2000 census)Languages:Filipino (official; based on Tagalog) and English (official); eight major dialects - Tagalog, Cebuano, Ilocano, Hiligaynon or Ilonggo, Bicol, Waray, Pampango, and PangasinanReligions:Catholic 82.9% (Roman Catholic 80.9%, Aglipayan 2%), Muslim 5%, Evangelical 2.8%, Iglesia ni Kristo 2.3%, other Christian 4.5%, other 1.8%, unspecified 0.6%, none 0.1% (2000 census)Population:105,720,644 (July 2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 12Age structure:0-14 years: 34% (male 18,339,398/female 17,607,472)15-24 years: 19.1% (male 10,259,385/female 9,896,090)25-54 years: 36.8% (male 19,550,257/female 19,369,177)55-64 years: 5.7% (male 2,772,003/female 3,239,659)65 years and over: 4.4% (male 2,023,118/female 2,664,085) (2013 est.)Dependency ratios:total dependency ratio: 61.4 %youth dependency ratio: 55.1 %elderly dependency ratio: 6.3 %potential support ratio: 15.9 (2013)Median age:total: 23.3 yearsmale: 22.8 yearsfemale: 23.8 years (2013 est.)Population growth rate:1.84% (2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 64Birth rate:24.62 births/1,000 population (2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 60Death rate:4.95 deaths/1,000 population (2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 187Net migration rate:-1.25 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 153Urbanization:urban population: 48.8% of total population (2011)rate of urbanization: 2.16% annual rate of change (2010-15 est.)Major urban areas - population:MANILA (capital) 11.449 million; Davao 1.48 million; Cebu City 845,000; Zamboanga 827,000 (2009)Sex ratio:at birth: 1.05 male(s)/female0-14 years: 1.04 male(s)/female15-24 years: 1.04 male(s)/female25-54 years: 1.01 male(s)/female55-64 years: 0.86 male(s)/female65 years and over: 0.76 male(s)/femaletotal population: 1 male(s)/female (2013 est.)Mother's mean age at first birth:23.1 (2008 est.)Maternal mortality rate:99 deaths/100,000 live births (2010)country comparison to the world: 75Infant mortality rate:total: 18.19 deaths/1,000 live birthscountry comparison to the world: 99male: 20.59 deaths/1,000 live birthsfemale: 15.66 deaths/1,000 live births (2013 est.)Life expectancy at birth:total population: 72.21 yearscountry comparison to the world: 135male: 69.26 yearsfemale: 75.31 years (2013 est.)Total fertility rate:3.1 children born/woman (2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 53Contraceptive prevalence rate:48.9% (2011)Health expenditures:3.6% of GDP (2010)country comparison to the world: 174Physicians density:1.15 physicians/1,000 population (2004)Hospital bed density:0.5 beds/1,000 population (2009)Drinking water source:improved:urban: 93% of populationrural: 92% of populationtotal: 92% of populationunimproved:urban: 7% of populationrural: 8% of populationtotal: 8% of population (2010 est.)Sanitation facility access:improved:urban: 79% of populationrural: 69% of populationtotal: 74% of populationunimproved:urban: 21% of populationrural: 31% of populationtotal: 26% of population (2010 est.)HIV/AIDS - adult prevalence rate:less than 0.1% (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 155HIV/AIDS - people living with HIV/AIDS:8,700 (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 104HIV/AIDS - deaths:fewer than 200 (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 109Major infectious diseases:degree of risk: highfood or waterborne diseases: bacterial diarrhea, hepatitis A, and typhoid fevervectorborne diseases: dengue fever and malariawater contact disease: leptospirosis (2013)Obesity - adult prevalence rate:6.3% (2008)country comparison to the world: 148Children under the age of 5 years underweight:20.7% (2008)country comparison to the world: 30Education expenditures:2.7% of GDP (2009)country comparison to the world: 151Literacy:definition: age 15 and over can read and writetotal population: 95.4%male: 95%female: 95.8% (2008 est.)School life expectancy (primary to tertiary education):total: 11 yearsmale: 11 yearsfemale: 12 years (2009)Unemployment, youth ages 15-24:total: 17.4%country comparison to the world: 74male: 16.2%female: 19.3% (2009)Government ::PhilippinesCountry name:conventional long form: Republic of the Philippinesconventional short form: Philippineslocal long form: Republika ng Pilipinaslocal short form: PilipinasGovernment type:republicCapital:name: Manilageographic coordinates: 14 36 N, 120 58 Etime difference: UTC+8 (13 hours ahead of Washington, DC during Standard Time)Administrative divisions:80 provinces and 39 chartered citiesprovinces: Abra, Agusan del Norte, Agusan del Sur, Aklan, Albay, Antique, Apayao, Aurora, Basilan, Bataan, Batanes, Batangas, Biliran, Benguet, Bohol, Bukidnon, Bulacan, Cagayan, Camarines Norte, Camarines Sur, Camiguin, Capiz, Catanduanes, Cavite, Cebu, Compostela, Davao del Norte, Davao del Sur, Davao Oriental, Dinagat Islands, Eastern Samar, Guimaras, Ifugao, Ilocos Norte, Ilocos Sur, Iloilo, Isabela, Kalinga, Laguna, Lanao del Norte, Lanao del Sur, La Union, Leyte, Maguindanao, Marinduque, Masbate, Mindoro Occidental, Mindoro Oriental, Misamis Occidental, Misamis Oriental, Mountain Province, Negros Occidental, Negros Oriental, North Cotabato, Northern Samar, Nueva Ecija, Nueva Vizcaya, Palawan, Pampanga, Pangasinan, Quezon, Quirino, Rizal, Romblon, Samar, Sarangani, Siquijor, Sorsogon, South Cotabato, Southern Leyte, Sultan Kudarat, Sulu, Surigao del Norte, Surigao del Sur, Tarlac, Tawi-Tawi, Zambales, Zamboanga del Norte, Zamboanga del Sur, Zamboanga Sibugaychartered cities: Angeles, Antipolo, Bacolod, Baguio, Butuan, Cagayan de Oro, Caloocan, Cebu, Cotabato, Dagupan, Davao, General Santos, Iligan, Iloilo, Lapu-Lapu, Las Pinas, Lucena, Makati, Malabon, Mandaluyong, Mandaue, Manila, Marikina, Muntinlupa, Naga, Navotas, Olongapo, Ormoc, Paranaque, Pasay, Pasig, Puerto Princesa, Quezon, San Juan, Santiago, Tacloban, Taguig, Valenzuela, Zamboanga (2012)Independence:12 June 1898 (independence proclaimed from Spain); 4 July 1946 (from the US)National holiday:Independence Day, 12 June (1898); note - 12 June 1898 was date of declaration of independence from Spain; 4 July 1946 was date of independence from USConstitution:2 February 1987, effective 11 February 1987Legal system:mixed legal system of civil, common, Islamic, and customary lawInternational law organization participation:accepts compulsory ICJ jurisdiction with reservations; accepts ICCt jurisdictionSuffrage:18 years of age; universalExecutive branch:chief of state: President Benigno AQUINO (since 30 June 2010); Vice President Jejomar BINAY (since 30 June 2010); note - president is both chief of state and head of governmenthead of government: President Benigno AQUINO (since 30 June 2010)cabinet: Cabinet appointed by the president with consent of Commission of Appointments(For more information visit the World Leaders website )elections: president and vice president elected on separate tickets by popular vote for a single six-year term; election held on 10 May 2010 (next election to be held in May 2016)election results: Benigno AQUINO elected president; percent of vote - Benigno AQUINO 42.1%, Joseph ESTRADA 26.3%, seven others 31.6%; Jejomar BINAY elected vice president; percent of vote Jejomar BINAY 41.6%, Manuel ROXAS 39.6%, six others 18.8%Legislative branch:bicameral Congress or Kongreso consists of the Senate or Senado (24 seats - one-half elected every three years; members elected at large by popular vote to serve six-year terms) and the House of Representatives or Kapulungan Ng Nga Kinatawan (287 seats - 230 members in one tier representing districts and 57 sectoral party-list members in a second tier representing special minorities elected on the basis of one seat for every 2% of the total vote but with each party limited to three seats); a party represented in one tier may not hold seats in the other tier; all House members are elected by popular vote to serve three-year termsnote: the constitution limits the House of Representatives to 250 members; the number of members allowed was increased, however, through legislation when in April 2009 the Philippine Supreme Court ruled that additional party members could sit in the House of Representatives if they received the required number of voteselections: Senate - elections last held on 13 May 2013 (next to be held in May 2016); House of Representatives - elections last held on 13 May 2013 (next to be held in May 2016)election results: Senate - percent of vote by party for 2013 election - UNA 26.94%, NP 15.3%, LP 11.32%, NPC 10.15%, LDP 5.38%, PDP-Laban 4.95%, others 9.72%, independents 16.24%; seats by party after 2013 election - UNA 5, NP 5, LP 4, Lakas 2, NPC 2, LDP 1, PDP-Laban 1, PRP 1, independents 3; House of Representatives - percent of vote by party - LP 38.3%, NPC 17.4%, UNA 11.4%, NUP 8.7%, NP 8.5%, Lakas 5.3%, independents 6.0%, others 4.4%; seats by party - LP 110, NPC 43, NUP 24, NP 17, Lakas 14, UNA 8, independents 6, others 12; party-list 57Judicial branch:highest court(s): Supreme Court (consists of a chief justice and 14 associate justices)judge selection and term of office: justices are appointed by the president on the recommendation of the Judicial and Bar Council, a constitutionally-created, 6-member body that recommends Supreme Court nominees; justices serve until age 70subordinate courts: Court of Appeals; Sandiganbayan (special court for corruption cases of government officials); Court of Tax Appeals; regional, metropolitan, and municipal trial courts; sharia courtsPolitical parties and leaders:Laban ng Demokratikong Pilipino (Struggle of Filipino Democrats) or LDP [Edgardo ANGARA]Lakas ng EDSA-Christian Muslim Democrats or Lakas-CMD [Manuel ""Mar"" ROXAS]Liberal Party or LP [Manuel ROXAS]Nacionalista Party or NP [Manuel ""Manny"" VILLAR]Nationalist People's Coalition or NPC [Frisco SAN JUAN]PDP-Laban [Aquilino PIMENTEL]People's Reform Party [Miriam Defensor SANTIAGO]Puwersa ng Masang Pilipino (Force of the Philippine Masses) or PMP [Joseph ESTRADA]note: United Nationalist Alliance or [UNA] - PDP-Laban and PMP coalition for the 2013 electionPolitical pressure groups and leaders:Black and White Movement [Vicente ROMANO]Kilosbayan [Jovito SALONGA]International organization participation:ADB, APEC, APT, ARF, ASEAN, BIS, CD, CICA (observer), CP, EAS, FAO, G-24, G-77, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICC (national committees), ICRM, IDA, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, IHO, ILO, IMF, IMO, IMSO, Interpol, IOC, IOM, IPU, ISO, ITSO, ITU, ITUC (NGOs), MIGA, MINUSTAH, NAM, OAS (observer), OPCW, PCA, PIF (partner), UN, UNCTAD, UNDOF, UNESCO, UNHCR, UNIDO, Union Latina, UNISFA, UNMIL, UNMISS, UNMIT, UNMOGIP, UNOCI, UNWTO, UPU, WCO, WFTU (NGOs), WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTODiplomatic representation in the US:chief of mission: Ambassador Jose L. CUISIA Jr.chancery: 1600 Massachusetts Avenue NW, Washington, DC 20036telephone: [1] (202) 467-9300FAX: [1] (202) 467-9417consulate(s) general: Chicago, Honolulu, Los Angeles, New York, San Francisco, Tamuning (Guam)Diplomatic representation from the US:chief of mission: Ambassador Harry K. THOMAS Jr.embassy: 1201 Roxas Boulevard, Ermita 1000, Manilamailing address: PSC 500, FPO AP 96515-1000telephone: [63] (2) 301-2000FAX: [63] (2) 301-2017Flag description:two equal horizontal bands of blue (top) and red; a white equilateral triangle is based on the hoist side; the center of the triangle displays a yellow sun with eight primary rays; each corner of the triangle contains a small, yellow, five-pointed star; blue stands for peace and justice, red symbolizes courage, the white equal-sided triangle represents equality; the rays recall the first eight provinces that sought independence from Spain, while the stars represent the three major geographical divisions of the country: Luzon, Visayas, and Mindanao; the design of the flag dates to 1897note: in wartime the flag is flown upside down with the red band at the topNational symbol(s):Philippine eagleNational anthem:name: ""Lupang Hinirang"" (Chosen Land)lyrics/music: Jose PALMA (revised by Felipe PADILLA de Leon)/Julian FELIPEnote: music adopted 1898, original Spanish lyrics adopted 1899, Filipino (Tagalog) lyrics adopted 1956; although the original lyrics were written in Spanish, later English and Filipino versions were created; today, only the Filipino version is usedEconomy ::PhilippinesEconomy - overview:Philippine GDP growth, which cooled from 7.6% in 2010 to 3.9% in 2011, expanded to 6.6% in 2012 - meeting the government's targeted 6%-7% growth range. The 2012 expansion partly reflected a rebound from depressed 2011 export and public sector spending levels. The economy has weathered global economic and financial downturns better than its regional peers due to minimal exposure to troubled international securities, lower dependence on exports, relatively resilient domestic consumption, large remittances from four- to five-million overseas Filipino workers, and a rapidly expanding business process outsourcing industry. The current account balance had recorded consecutive surpluses since 2003; international reserves are at record highs; the banking system is stable; and the stock market was Asia's second best-performer in 2012. Efforts to improve tax administration and expenditure management have helped ease the Philippines' tight fiscal situation and reduce high debt levels. The Philippines received several credit rating upgrades on its sovereign debt in 2012, and has had little difficulty tapping domestic and international markets to finance its deficits. Achieving a higher growth path nevertheless remains a pressing challenge. Economic growth in the Philippines averaged 4.5% during the MACAPAGAL-ARROYO administration but poverty worsened during her term. Growth has accelerated under the AQUINO government, but with limited progress thus far in bringing down unemployment, which hovers around 7%, and improving the quality of jobs. Underemployment is nearly 20% and more than 40% of the employed are estimated to be working in the informal sector. The AQUINO administration has been working to boost the budgets for education, health, cash transfers to the poor, and other social spending programs, and is relying on the private sector to help fund major infrastructure projects under its Public-Private Partnership program. Long term challenges include reforming governance and the judicial system, building infrastructure, improving regulatory predictability, and the ease of doing business, attracting higher levels of local and foreign investments. The Philippine Constitution and the other laws continue to restrict foreign ownership in important activities/sectors (such as land ownership and public utilities).GDP (purchasing power parity):$431.3 billion (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 32$404.7 billion (2011 est.)$389.4 billion (2010 est.)note: data are in 2012 US dollarsGDP (official exchange rate):$250.4 billion (2012 est.)GDP - real growth rate:6.6% (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 333.9% (2011 est.)7.6% (2010 est.)GDP - per capita (PPP):$4,500 (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 165$4,300 (2011 est.)$4,200 (2010 est.)note: data are in 2012 US dollarsGross national saving:21.3% of GDP (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 6623.6% of GDP (2011 est.)25% of GDP (2010 est.)GDP - composition, by end use:household consumption: 74.2%government consumption: 10.5%investment in fixed capital: 19.4%investment in inventories: -0.9%exports of goods and services: 30.8%imports of goods and services: -34%(2012 est.)GDP - composition, by sector of origin:agriculture: 11.8%industry: 31.1%services: 57.1% (2012 est.)Agriculture - products:sugarcane, coconuts, rice, corn, bananas, cassavas, pineapples, mangoes; pork, eggs, beef; fishIndustries:electronics assembly, garments, footwear, pharmaceuticals, chemicals, wood products, food processing, petroleum refining, fishingIndustrial production growth rate:6.8% (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 30Labor force:40.42 million (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 16Labor force - by occupation:agriculture: 32%industry: 15%services: 53% (2012 est.)Unemployment rate:7% (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 787% (2011 est.)Population below poverty line:26.5% (2009 est.)Household income or consumption by percentage share:lowest 10%: 2.6%highest 10%: 33.6% (2009 est.)Distribution of family income - Gini index:44.8 (2009)country comparison to the world: 4246.6 (2003)Budget:revenues: $36.35 billionexpenditures: $42.1 billion (2012 est.)Taxes and other revenues:14.5% of GDP (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 195Budget surplus (+) or deficit (-):-2.3% of GDP (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 92Public debt:51.5% of GDP (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 6351% of GDP (2011 est.)note: data cover debt issued by the national government, and excludes debt instruments issued by government entities other than the treasury; the data include treasury debt held by foreign entities; the data exclude debt issued by social security institutions, government-owned and controlled corporations, the Central Bank, and local government unitsFiscal year:calendar yearInflation rate (consumer prices):3.1% (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 974.7% (2011 est.)Central bank discount rate:5.3% (31 December 2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 645.6% (31 December 2011 est.)Commercial bank prime lending rate:5.68% (31 December 2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 1346.66% (31 December 2011 est.)Stock of narrow money:$38.93 billion (31 December 2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 54$33.97 billion (31 December 2011 est.)Stock of broad money:$132.5 billion (31 December 2011 est.)country comparison to the world: 51$126 billion (31 December 2010 est.)Stock of domestic credit:$129.4 billion (31 December 2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 49$112.6 billion (31 December 2011 est.)Market value of publicly traded shares:$266.3 billion (31 December 2012)country comparison to the world: 35$198.4 billion (31 December 2011)$202.2 billion (31 December 2010)Current account balance:$9.65 billion (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 26$6.988 billion (2011 est.)Exports:$46.28 billion (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 60$38.28 billion (2011 est.)Exports - commodities:semiconductors and electronic products, transport equipment, garments, copper products, petroleum products, coconut oil, fruitsExports - partners:Japan 19%, US 14.2%, China 11.8%, Singapore 9.4%, Hong Kong 9.2%, South Korea 5.5%, Thailand 4.7% (2012)Imports:$61.49 billion (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 48$55.25 billion (2011 est.)Imports - commodities:electronic products, mineral fuels, machinery and transport equipment, iron and steel, textile fabrics, grains, chemicals, plasticImports - partners:US 11.5%, China 10.8%, Japan 10.4%, South Korea 7.3%, Singapore 7.1%, Thailand 5.6%, Saudi Arabia 5.6%, Indonesia 4.4%, Malaysia 4% (2012)Reserves of foreign exchange and gold:$83.83 billion (31 December 2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 27$75.3 billion (31 December 2011 est.)Debt - external:$74.87 billion (31 December 2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 54$76.04 billion (31 December 2011 est.)Stock of direct foreign investment - at home:$30.38 billion (31 December 2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 60$27.58 billion (31 December 2011 est.)Stock of direct foreign investment - abroad:$8.435 billion (31 December 2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 57$6.59 billion (31 December 2011 est.)Exchange rates:Philippine pesos (PHP) per US dollar -42.229 (2012 est.)43.313 (2011 est.)45.11 (2010 est.)47.68 (2009)44.439 (2008)Energy ::PhilippinesElectricity - production:67.74 billion kWh (2010 est.)country comparison to the world: 41Electricity - consumption:64.52 billion kWh (2010 est.)country comparison to the world: 39Electricity - exports:0 kWh (2010 est.)country comparison to the world: 120Electricity - imports:0 kWh (2010 est.)country comparison to the world: 123Electricity - installed generating capacity:16.36 million kW (2010 est.)country comparison to the world: 42Electricity - from fossil fuels:66.1% of total installed capacity (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 119Electricity - from nuclear fuels:0% of total installed capacity (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 166Electricity - from hydroelectric plants:21.1% of total installed capacity (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 88Electricity - from other renewable sources:12.8% of total installed capacity (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 17Crude oil - production:26,640 bbl/day (2011 est.)country comparison to the world: 68Crude oil - exports:28,090 bbl/day (2010 est.)country comparison to the world: 51Crude oil - imports:176,000 bbl/day (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 36Crude oil - proved reserves:138.5 million bbl (1 January 2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 69Refined petroleum products - production:181,300 bbl/day (2010 est.)country comparison to the world: 57Refined petroleum products - consumption:315,600 bbl/day (2011 est.)country comparison to the world: 42Refined petroleum products - exports:17,810 bbl/day (2010 est.)country comparison to the world: 74Refined petroleum products - imports:147,900 bbl/day (2010 est.)country comparison to the world: 38Natural gas - production:3.91 billion cu m (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 52Natural gas - consumption:2.86 billion cu m (2010)country comparison to the world: 73Natural gas - exports:0 cu m (2010)country comparison to the world: 167Natural gas - imports:0 cu m (2010)country comparison to the world: 120Natural gas - proved reserves:98.54 billion cu m (1 January 2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 53Carbon dioxide emissions from consumption of energy:85.63 million Mt (2010 est.)country comparison to the world: 41Communications ::PhilippinesTelephones - main lines in use:3.556 million (2011)country comparison to the world: 45Telephones - mobile cellular:94.19 million (2011)country comparison to the world: 14Telephone system:general assessment: good international radiotelephone and submarine cable services; domestic and interisland service adequatedomestic: telecommunications infrastructure includes the following platforms: fixed-line, mobile cellular, cable TV, over-the-air TV, radio and Very Small Aperture Terminal (VSAT), fiber-optic cable, and satellite; mobile-cellular communications now dominate the industryinternational: country code - 63; a series of submarine cables together provide connectivity to Asia, US, the Middle East, and Europe; multiple international gateways (2011)Broadcast media:multiple national private TV and radio networks; multi-channel satellite and cable TV systems available; more than 350 TV stations - 4 major TV networks operating nationwide with 1 being government-owned; some 1100 cable TV providers and some 1,200 radio stations broadcasting; the Philippines is scheduled to complete the switch from analog to digital broadcasting by the end of 2015 (2012)Internet country code:.phInternet hosts:425,812 (2012)country comparison to the world: 52Internet users:8.278 million (2009)country comparison to the world: 34Transportation ::PhilippinesAirports:247 (2013)country comparison to the world: 24Airports - with paved runways:total: 89over 3,047 m: 42,438 to 3,047 m: 81,524 to 2,437 m: 33914 to 1,523 m: 34under 914 m: 10 (2013)Airports - with unpaved runways:total: 1581,524 to 2,437 m: 3914 to 1,523 m: 56under 914 m:99 (2013)Heliports:2 (2013)Pipelines:gas 567 km; oil 138 km; refined products 185 km (2013)Railways:total: 995 kmcountry comparison to the world: 88narrow gauge: 995 km 1.067-m gauge (484 km are in operation) (2010)Roadways:total: 213,151 kmcountry comparison to the world: 23paved: 54,481 kmunpaved: 158,670 km (2009)Waterways:3,219 km (limited to vessels with draft less than 1.5 m) (2011)country comparison to the world: 31Merchant marine:total: 446country comparison to the world: 23by type: bulk carrier 76, cargo 152, carrier 12, chemical tanker 27, container 17, liquefied gas 5, passenger 7, passenger/cargo 65, petroleum tanker 44, refrigerated cargo 20, roll on/roll off 11, vehicle carrier 10foreign-owned: 159 (Bermuda 47, China 4, Denmark 2, Germany 2, Greece 5, Japan 77, Malaysia 1, Netherlands 17, Singapore 1, South Korea 1, Taiwan 1, UAE 1)registered in other countries: 7 (Cyprus 1, Panama 5, unknown 1) (2010)Ports and terminals:Batangas, Cagayan de Oro, Cebu, Davao, Liman, ManilaTransportation - note:the International Maritime Bureau reports the territorial and offshore waters in the South China Sea as high risk for piracy and armed robbery against ships; numerous commercial vessels have been attacked and hijacked both at anchor and while underway; hijacked vessels are often disguised and cargo diverted to ports in East Asia; crews have been murdered or cast adriftMilitary ::PhilippinesMilitary branches:Armed Forces of the Philippines (AFP): Army, Navy (includes Marine Corps), Air Force (2013)Military service age and obligation:17-23 years of age (officers 20-24) for voluntary military service; no conscription; applicants must be single male or female Philippine citizens with either 72 college credit hours (enlisted) or a baccalaureate degree (officers) (2013)Manpower available for military service:males age 16-49: 25,614,135females age 16-49: 25,035,061 (2010 est.)Manpower fit for military service:males age 16-49: 20,142,940females age 16-49: 21,427,792 (2010 est.)Manpower reaching militarily significant age annually:male: 1,060,319female: 1,021,069 (2010 est.)Military expenditures:0.9% of GDP (2005 est.)country comparison to the world: 139Transnational Issues ::PhilippinesDisputes - international:Philippines claims sovereignty over Scarborough Reef (also claimed by China together with Taiwan) and over certain of the Spratly Islands, known locally as the Kalayaan (Freedom) Islands, also claimed by China, Malaysia, Taiwan, and Vietnam; the 2002 ""Declaration on the Conduct of Parties in the South China Sea,"" has eased tensions in the Spratly Islands but falls short of a legally binding ""code of conduct"" desired by several of the disputants; in March 2005, the national oil companies of China, the Philippines, and Vietnam signed a joint accord to conduct marine seismic activities in the Spratly Islands; Philippines retains a dormant claim to Malaysia's Sabah State in northern Borneo based on the Sultanate of Sulu's granting the Philippines Government power of attorney to pursue a sovereignty claim on his behalf; maritime delimitation negotiations continue with PalauRefugees and internally displaced persons:IDPs: at least 843,000 (government troops fighting the Moro Islamic Liberation Front, the Abu Sayyaf Group, and the New People's Army; clan feuds; natural disasters (December 2012 Typhoon Bopha)) (2013)stateless persons: 6,015 (2012)Illicit drugs:domestic methamphetamine production has been a growing problem in recent years despite government crackdowns; major consumer of amphetamines; longstanding marijuana producer mainly in rural areas where Manila's control is limited"
Introduction ::PhilippinesBackground:The Philippine Islands became a Spanish colony during the 16th century; they were ceded to the US in 1898 following the Spanish-American War. In 1935 the Philippines became a self-governing commonwealth. Manuel QUEZON was elected president and was tasked with preparing the country for independence after a 10-year transition. In 1942 the islands fell under Japanese occupation during World War II, and US forces and Filipinos fought together during 1944-45 to regain control. On 4 July 1946 the Republic of the Philippines attained its independence. A 20-year rule by Ferdinand MARCOS ended in 1986, when a ""people power"" movement in Manila (""EDSA 1"") forced him into exile and installed Corazon AQUINO as president. Her presidency was hampered by several coup attempts that prevented a return to full political stability and economic development. Fidel RAMOS was elected president in 1992. His administration was marked by increased stability and by progress on economic reforms. In 1992, the US closed its last military bases on the islands. Joseph ESTRADA was elected president in 1998. He was succeeded by his vice-president, Gloria MACAPAGAL-ARROYO, in January 2001 after ESTRADA's stormy impeachment trial on corruption charges broke down and another ""people power"" movement (""EDSA 2"") demanded his resignation. MACAPAGAL-ARROYO was elected to a six-year term as president in May 2004. Her presidency was marred by several corruption allegations but the Philippine economy was one of the few to avoid contraction following the 2008 global financial crisis, expanding each year of her administration. Benigno AQUINO III was elected to a six-year term as president in May 2010. The Philippine Government faces threats from several groups, some of which are on the US Government's Foreign Terrorist Organization list. Manila has waged a decades-long struggle against ethnic Moro insurgencies in the southern Philippines, which has led to a peace accord with the Moro National Liberation Front and ongoing peace talks with the Moro Islamic Liberation Front. The decades-long Maoist-inspired New People's Army insurgency also operates through much of the country. The Philippines faces increased tension with China over disputed territorial and maritime claims in the South China Sea.Geography ::PhilippinesLocation:Southeastern Asia, archipelago between the Philippine Sea and the South China Sea, east of VietnamGeographic coordinates:13 00 N, 122 00 EArea:total: 300,000 sq kmcountry comparison to the world: 73land: 298,170 sq kmwater: 1,830 sq kmArea - comparative:slightly larger than ArizonaLand boundaries:0 kmCoastline:36,289 kmMaritime claims:territorial sea: irregular polygon extending up to 100 nm from coastline as defined by 1898 treaty; since late 1970s has also claimed polygonal-shaped area in South China Sea up to 285 nm in breadthexclusive economic zone: 200 nmcontinental shelf: to depth of exploitationClimate:tropical marine; northeast monsoon (November to April); southwest monsoon (May to October)Terrain:mostly mountains with narrow to extensive coastal lowlandsElevation extremes:lowest point: Philippine Sea 0 mhighest point: Mount Apo 2,954 mNatural resources:timber, petroleum, nickel, cobalt, silver, gold, salt, copperLand use:arable land: 18%permanent crops: 17.33%other: 64.67% (2011)Irrigated land:18,790 sq km (2006)Total renewable water resources:479 cu km (2011)Freshwater withdrawal (domestic/industrial/agricultural):total: 81.56 cu km/yr (8%/10%/82%)per capita: 859.9 cu m/yr (2009)Natural hazards:astride typhoon belt, usually affected by 15 and struck by five to six cyclonic storms each year; landslides; active volcanoes; destructive earthquakes; tsunamisvolcanism: significant volcanic activity; Taal (elev. 311 m), which has shown recent unrest and may erupt in the near future, has been deemed a ""Decade Volcano"" by the International Association of Volcanology and Chemistry of the Earth's Interior, worthy of study due to its explosive history and close proximity to human populations; Mayon (elev. 2,462 m), the country's most active volcano, erupted in 2009 forcing over 33,000 to be evacuated; other historically active volcanoes include Biliran, Babuyan Claro, Bulusan, Camiguin, Camiguin de Babuyanes, Didicas, Iraya, Jolo, Kanlaon, Makaturing, Musuan, Parker, Pinatubo and RagangEnvironment - current issues:uncontrolled deforestation especially in watershed areas; soil erosion; air and water pollution in major urban centers; coral reef degradation; increasing pollution of coastal mangrove swamps that are important fish breeding groundsEnvironment - international agreements:party to: Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification, Endangered Species, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Marine Dumping, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Tropical Timber 83, Tropical Timber 94, Wetlands, Whalingsigned, but not ratified: Air Pollution-Persistent Organic PollutantsGeography - note:the Philippine archipelago is made up of 7,107 islands; favorably located in relation to many of Southeast Asia's main water bodies: the South China Sea, Philippine Sea, Sulu Sea, Celebes Sea, and Luzon StraitPeople and Society ::PhilippinesNationality:noun: Filipino(s)adjective: PhilippineEthnic groups:Tagalog 28.1%, Cebuano 13.1%, Ilocano 9%, Bisaya/Binisaya 7.6%, Hiligaynon Ilonggo 7.5%, Bikol 6%, Waray 3.4%, other 25.3% (2000 census)Languages:Filipino (official; based on Tagalog) and English (official); eight major dialects - Tagalog, Cebuano, Ilocano, Hiligaynon or Ilonggo, Bicol, Waray, Pampango, and PangasinanReligions:Catholic 82.9% (Roman Catholic 80.9%, Aglipayan 2%), Muslim 5%, Evangelical 2.8%, Iglesia ni Kristo 2.3%, other Christian 4.5%, other 1.8%, unspecified 0.6%, none 0.1% (2000 census)Population:105,720,644 (July 2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 12Age structure:0-14 years: 34% (male 18,339,398/female 17,607,472)15-24 years: 19.1% (male 10,259,385/female 9,896,090)25-54 years: 36.8% (male 19,550,257/female 19,369,177)55-64 years: 5.7% (male 2,772,003/female 3,239,659)65 years and over: 4.4% (male 2,023,118/female 2,664,085) (2013 est.)Dependency ratios:total dependency ratio: 61.4 %youth dependency ratio: 55.1 %elderly dependency ratio: 6.3 %potential support ratio: 15.9 (2013)Median age:total: 23.3 yearsmale: 22.8 yearsfemale: 23.8 years (2013 est.)Population growth rate:1.84% (2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 64Birth rate:24.62 births/1,000 population (2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 60Death rate:4.95 deaths/1,000 population (2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 187Net migration rate:-1.25 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 153Urbanization:urban population: 48.8% of total population (2011)rate of urbanization: 2.16% annual rate of change (2010-15 est.)Major urban areas - population:MANILA (capital) 11.449 million; Davao 1.48 million; Cebu City 845,000; Zamboanga 827,000 (2009)Sex ratio:at birth: 1.05 male(s)/female0-14 years: 1.04 male(s)/female15-24 years: 1.04 male(s)/female25-54 years: 1.01 male(s)/female55-64 years: 0.86 male(s)/female65 years and over: 0.76 male(s)/femaletotal population: 1 male(s)/female (2013 est.)Mother's mean age at first birth:23.1 (2008 est.)Maternal mortality rate:99 deaths/100,000 live births (2010)country comparison to the world: 75Infant mortality rate:total: 18.19 deaths/1,000 live birthscountry comparison to the world: 99male: 20.59 deaths/1,000 live birthsfemale: 15.66 deaths/1,000 live births (2013 est.)Life expectancy at birth:total population: 72.21 yearscountry comparison to the world: 135male: 69.26 yearsfemale: 75.31 years (2013 est.)Total fertility rate:3.1 children born/woman (2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 53Contraceptive prevalence rate:48.9% (2011)Health expenditures:3.6% of GDP (2010)country comparison to the world: 174Physicians density:1.15 physicians/1,000 population (2004)Hospital bed density:0.5 beds/1,000 population (2009)Drinking water source:improved:urban: 93% of populationrural: 92% of populationtotal: 92% of populationunimproved:urban: 7% of populationrural: 8% of populationtotal: 8% of population (2010 est.)Sanitation facility access:improved:urban: 79% of populationrural: 69% of populationtotal: 74% of populationunimproved:urban: 21% of populationrural: 31% of populationtotal: 26% of population (2010 est.)HIV/AIDS - adult prevalence rate:less than 0.1% (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 155HIV/AIDS - people living with HIV/AIDS:8,700 (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 104HIV/AIDS - deaths:fewer than 200 (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 109Major infectious diseases:degree of risk: highfood or waterborne diseases: bacterial diarrhea, hepatitis A, and typhoid fevervectorborne diseases: dengue fever and malariawater contact disease: leptospirosis (2013)Obesity - adult prevalence rate:6.3% (2008)country comparison to the world: 148Children under the age of 5 years underweight:20.7% (2008)country comparison to the world: 30Education expenditures:2.7% of GDP (2009)country comparison to the world: 151Literacy:definition: age 15 and over can read and writetotal population: 95.4%male: 95%female: 95.8% (2008 est.)School life expectancy (primary to tertiary education):total: 11 yearsmale: 11 yearsfemale: 12 years (2009)Unemployment, youth ages 15-24:total: 17.4%country comparison to the world: 74male: 16.2%female: 19.3% (2009)Government ::PhilippinesCountry name:conventional long form: Republic of the Philippinesconventional short form: Philippineslocal long form: Republika ng Pilipinaslocal short form: PilipinasGovernment type:republicCapital:name: Manilageographic coordinates: 14 36 N, 120 58 Etime difference: UTC+8 (13 hours ahead of Washington, DC during Standard Time)Administrative divisions:80 provinces and 39 chartered citiesprovinces: Abra, Agusan del Norte, Agusan del Sur, Aklan, Albay, Antique, Apayao, Aurora, Basilan, Bataan, Batanes, Batangas, Biliran, Benguet, Bohol, Bukidnon, Bulacan, Cagayan, Camarines Norte, Camarines Sur, Camiguin, Capiz, Catanduanes, Cavite, Cebu, Compostela, Davao del Norte, Davao del Sur, Davao Oriental, Dinagat Islands, Eastern Samar, Guimaras, Ifugao, Ilocos Norte, Ilocos Sur, Iloilo, Isabela, Kalinga, Laguna, Lanao del Norte, Lanao del Sur, La Union, Leyte, Maguindanao, Marinduque, Masbate, Mindoro Occidental, Mindoro Oriental, Misamis Occidental, Misamis Oriental, Mountain Province, Negros Occidental, Negros Oriental, North Cotabato, Northern Samar, Nueva Ecija, Nueva Vizcaya, Palawan, Pampanga, Pangasinan, Quezon, Quirino, Rizal, Romblon, Samar, Sarangani, Siquijor, Sorsogon, South Cotabato, Southern Leyte, Sultan Kudarat, Sulu, Surigao del Norte, Surigao del Sur, Tarlac, Tawi-Tawi, Zambales, Zamboanga del Norte, Zamboanga del Sur, Zamboanga Sibugaychartered cities: Angeles, Antipolo, Bacolod, Baguio, Butuan, Cagayan de Oro, Caloocan, Cebu, Cotabato, Dagupan, Davao, General Santos, Iligan, Iloilo, Lapu-Lapu, Las Pinas, Lucena, Makati, Malabon, Mandaluyong, Mandaue, Manila, Marikina, Muntinlupa, Naga, Navotas, Olongapo, Ormoc, Paranaque, Pasay, Pasig, Puerto Princesa, Quezon, San Juan, Santiago, Tacloban, Taguig, Valenzuela, Zamboanga (2012)Independence:12 June 1898 (independence proclaimed from Spain); 4 July 1946 (from the US)National holiday:Independence Day, 12 June (1898); note - 12 June 1898 was date of declaration of independence from Spain; 4 July 1946 was date of independence from USConstitution:2 February 1987, effective 11 February 1987Legal system:mixed legal system of civil, common, Islamic, and customary lawInternational law organization participation:accepts compulsory ICJ jurisdiction with reservations; accepts ICCt jurisdictionSuffrage:18 years of age; universalExecutive branch:chief of state: President Benigno AQUINO (since 30 June 2010); Vice President Jejomar BINAY (since 30 June 2010); note - president is both chief of state and head of governmenthead of government: President Benigno AQUINO (since 30 June 2010)cabinet: Cabinet appointed by the president with consent of Commission of Appointments(For more information visit the World Leaders website )elections: president and vice president elected on separate tickets by popular vote for a single six-year term; election held on 10 May 2010 (next election to be held in May 2016)election results: Benigno AQUINO elected president; percent of vote - Benigno AQUINO 42.1%, Joseph ESTRADA 26.3%, seven others 31.6%; Jejomar BINAY elected vice president; percent of vote Jejomar BINAY 41.6%, Manuel ROXAS 39.6%, six others 18.8%Legislative branch:bicameral Congress or Kongreso consists of the Senate or Senado (24 seats - one-half elected every three years; members elected at large by popular vote to serve six-year terms) and the House of Representatives or Kapulungan Ng Nga Kinatawan (287 seats - 230 members in one tier representing districts and 57 sectoral party-list members in a second tier representing special minorities elected on the basis of one seat for every 2% of the total vote but with each party limited to three seats); a party represented in one tier may not hold seats in the other tier; all House members are elected by popular vote to serve three-year termsnote: the constitution limits the House of Representatives to 250 members; the number of members allowed was increased, however, through legislation when in April 2009 the Philippine Supreme Court ruled that additional party members could sit in the House of Representatives if they received the required number of voteselections: Senate - elections last held on 13 May 2013 (next to be held in May 2016); House of Representatives - elections last held on 13 May 2013 (next to be held in May 2016)election results: Senate - percent of vote by party for 2013 election - UNA 26.94%, NP 15.3%, LP 11.32%, NPC 10.15%, LDP 5.38%, PDP-Laban 4.95%, others 9.72%, independents 16.24%; seats by party after 2013 election - UNA 5, NP 5, LP 4, Lakas 2, NPC 2, LDP 1, PDP-Laban 1, PRP 1, independents 3; House of Representatives - percent of vote by party - LP 38.3%, NPC 17.4%, UNA 11.4%, NUP 8.7%, NP 8.5%, Lakas 5.3%, independents 6.0%, others 4.4%; seats by party - LP 110, NPC 43, NUP 24, NP 17, Lakas 14, UNA 8, independents 6, others 12; party-list 57Judicial branch:highest court(s): Supreme Court (consists of a chief justice and 14 associate justices)judge selection and term of office: justices are appointed by the president on the recommendation of the Judicial and Bar Council, a constitutionally-created, 6-member body that recommends Supreme Court nominees; justices serve until age 70subordinate courts: Court of Appeals; Sandiganbayan (special court for corruption cases of government officials); Court of Tax Appeals; regional, metropolitan, and municipal trial courts; sharia courtsPolitical parties and leaders:Laban ng Demokratikong Pilipino (Struggle of Filipino Democrats) or LDP [Edgardo ANGARA]Lakas ng EDSA-Christian Muslim Democrats or Lakas-CMD [Manuel ""Mar"" ROXAS]Liberal Party or LP [Manuel ROXAS]Nacionalista Party or NP [Manuel ""Manny"" VILLAR]Nationalist People's Coalition or NPC [Frisco SAN JUAN]PDP-Laban [Aquilino PIMENTEL]People's Reform Party [Miriam Defensor SANTIAGO]Puwersa ng Masang Pilipino (Force of the Philippine Masses) or PMP [Joseph ESTRADA]note: United Nationalist Alliance or [UNA] - PDP-Laban and PMP coalition for the 2013 electionPolitical pressure groups and leaders:Black and White Movement [Vicente ROMANO]Kilosbayan [Jovito SALONGA]International organization participation:ADB, APEC, APT, ARF, ASEAN, BIS, CD, CICA (observer), CP, EAS, FAO, G-24, G-77, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICC (national committees), ICRM, IDA, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, IHO, ILO, IMF, IMO, IMSO, Interpol, IOC, IOM, IPU, ISO, ITSO, ITU, ITUC (NGOs), MIGA, MINUSTAH, NAM, OAS (observer), OPCW, PCA, PIF (partner), UN, UNCTAD, UNDOF, UNESCO, UNHCR, UNIDO, Union Latina, UNISFA, UNMIL, UNMISS, UNMIT, UNMOGIP, UNOCI, UNWTO, UPU, WCO, WFTU (NGOs), WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTODiplomatic representation in the US:chief of mission: Ambassador Jose L. CUISIA Jr.chancery: 1600 Massachusetts Avenue NW, Washington, DC 20036telephone: [1] (202) 467-9300FAX: [1] (202) 467-9417consulate(s) general: Chicago, Honolulu, Los Angeles, New York, San Francisco, Tamuning (Guam)Diplomatic representation from the US:chief of mission: Ambassador Harry K. THOMAS Jr.embassy: 1201 Roxas Boulevard, Ermita 1000, Manilamailing address: PSC 500, FPO AP 96515-1000telephone: [63] (2) 301-2000FAX: [63] (2) 301-2017Flag description:two equal horizontal bands of blue (top) and red; a white equilateral triangle is based on the hoist side; the center of the triangle displays a yellow sun with eight primary rays; each corner of the triangle contains a small, yellow, five-pointed star; blue stands for peace and justice, red symbolizes courage, the white equal-sided triangle represents equality; the rays recall the first eight provinces that sought independence from Spain, while the stars represent the three major geographical divisions of the country: Luzon, Visayas, and Mindanao; the design of the flag dates to 1897note: in wartime the flag is flown upside down with the red band at the topNational symbol(s):Philippine eagleNational anthem:name: ""Lupang Hinirang"" (Chosen Land)lyrics/music: Jose PALMA (revised by Felipe PADILLA de Leon)/Julian FELIPEnote: music adopted 1898, original Spanish lyrics adopted 1899, Filipino (Tagalog) lyrics adopted 1956; although the original lyrics were written in Spanish, later English and Filipino versions were created; today, only the Filipino version is usedEconomy ::PhilippinesEconomy - overview:Philippine GDP growth, which cooled from 7.6% in 2010 to 3.9% in 2011, expanded to 6.6% in 2012 - meeting the government's targeted 6%-7% growth range. The 2012 expansion partly reflected a rebound from depressed 2011 export and public sector spending levels. The economy has weathered global economic and financial downturns better than its regional peers due to minimal exposure to troubled international securities, lower dependence on exports, relatively resilient domestic consumption, large remittances from four- to five-million overseas Filipino workers, and a rapidly expanding business process outsourcing industry. The current account balance had recorded consecutive surpluses since 2003; international reserves are at record highs; the banking system is stable; and the stock market was Asia's second best-performer in 2012. Efforts to improve tax administration and expenditure management have helped ease the Philippines' tight fiscal situation and reduce high debt levels. The Philippines received several credit rating upgrades on its sovereign debt in 2012, and has had little difficulty tapping domestic and international markets to finance its deficits. Achieving a higher growth path nevertheless remains a pressing challenge. Economic growth in the Philippines averaged 4.5% during the MACAPAGAL-ARROYO administration but poverty worsened during her term. Growth has accelerated under the AQUINO government, but with limited progress thus far in bringing down unemployment, which hovers around 7%, and improving the quality of jobs. Underemployment is nearly 20% and more than 40% of the employed are estimated to be working in the informal sector. The AQUINO administration has been working to boost the budgets for education, health, cash transfers to the poor, and other social spending programs, and is relying on the private sector to help fund major infrastructure projects under its Public-Private Partnership program. Long term challenges include reforming governance and the judicial system, building infrastructure, improving regulatory predictability, and the ease of doing business, attracting higher levels of local and foreign investments. The Philippine Constitution and the other laws continue to restrict foreign ownership in important activities/sectors (such as land ownership and public utilities).GDP (purchasing power parity):$431.3 billion (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 32$404.7 billion (2011 est.)$389.4 billion (2010 est.)note: data are in 2012 US dollarsGDP (official exchange rate):$250.4 billion (2012 est.)GDP - real growth rate:6.6% (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 333.9% (2011 est.)7.6% (2010 est.)GDP - per capita (PPP):$4,500 (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 165$4,300 (2011 est.)$4,200 (2010 est.)note: data are in 2012 US dollarsGross national saving:21.3% of GDP (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 6623.6% of GDP (2011 est.)25% of GDP (2010 est.)GDP - composition, by end use:household consumption: 74.2%government consumption: 10.5%investment in fixed capital: 19.4%investment in inventories: -0.9%exports of goods and services: 30.8%imports of goods and services: -34%(2012 est.)GDP - composition, by sector of origin:agriculture: 11.8%industry: 31.1%services: 57.1% (2012 est.)Agriculture - products:sugarcane, coconuts, rice, corn, bananas, cassavas, pineapples, mangoes; pork, eggs, beef; fishIndustries:electronics assembly, garments, footwear, pharmaceuticals, chemicals, wood products, food processing, petroleum refining, fishingIndustrial production growth rate:6.8% (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 30Labor force:40.42 million (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 16Labor force - by occupation:agriculture: 32%industry: 15%services: 53% (2012 est.)Unemployment rate:7% (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 787% (2011 est.)Population below poverty line:26.5% (2009 est.)Household income or consumption by percentage share:lowest 10%: 2.6%highest 10%: 33.6% (2009 est.)Distribution of family income - Gini index:44.8 (2009)country comparison to the world: 4246.6 (2003)Budget:revenues: $36.35 billionexpenditures: $42.1 billion (2012 est.)Taxes and other revenues:14.5% of GDP (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 195Budget surplus (+) or deficit (-):-2.3% of GDP (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 92Public debt:51.5% of GDP (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 6351% of GDP (2011 est.)note: data cover debt issued by the national government, and excludes debt instruments issued by government entities other than the treasury; the data include treasury debt held by foreign entities; the data exclude debt issued by social security institutions, government-owned and controlled corporations, the Central Bank, and local government unitsFiscal year:calendar yearInflation rate (consumer prices):3.1% (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 974.7% (2011 est.)Central bank discount rate:5.3% (31 December 2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 645.6% (31 December 2011 est.)Commercial bank prime lending rate:5.68% (31 December 2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 1346.66% (31 December 2011 est.)Stock of narrow money:$38.93 billion (31 December 2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 54$33.97 billion (31 December 2011 est.)Stock of broad money:$132.5 billion (31 December 2011 est.)country comparison to the world: 51$126 billion (31 December 2010 est.)Stock of domestic credit:$129.4 billion (31 December 2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 49$112.6 billion (31 December 2011 est.)Market value of publicly traded shares:$266.3 billion (31 December 2012)country comparison to the world: 35$198.4 billion (31 December 2011)$202.2 billion (31 December 2010)Current account balance:$9.65 billion (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 26$6.988 billion (2011 est.)Exports:$46.28 billion (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 60$38.28 billion (2011 est.)Exports - commodities:semiconductors and electronic products, transport equipment, garments, copper products, petroleum products, coconut oil, fruitsExports - partners:Japan 19%, US 14.2%, China 11.8%, Singapore 9.4%, Hong Kong 9.2%, South Korea 5.5%, Thailand 4.7% (2012)Imports:$61.49 billion (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 48$55.25 billion (2011 est.)Imports - commodities:electronic products, mineral fuels, machinery and transport equipment, iron and steel, textile fabrics, grains, chemicals, plasticImports - partners:US 11.5%, China 10.8%, Japan 10.4%, South Korea 7.3%, Singapore 7.1%, Thailand 5.6%, Saudi Arabia 5.6%, Indonesia 4.4%, Malaysia 4% (2012)Reserves of foreign exchange and gold:$83.83 billion (31 December 2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 27$75.3 billion (31 December 2011 est.)Debt - external:$74.87 billion (31 December 2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 54$76.04 billion (31 December 2011 est.)Stock of direct foreign investment - at home:$30.38 billion (31 December 2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 60$27.58 billion (31 December 2011 est.)Stock of direct foreign investment - abroad:$8.435 billion (31 December 2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 57$6.59 billion (31 December 2011 est.)Exchange rates:Philippine pesos (PHP) per US dollar -42.229 (2012 est.)43.313 (2011 est.)45.11 (2010 est.)47.68 (2009)44.439 (2008)Energy ::PhilippinesElectricity - production:67.74 billion kWh (2010 est.)country comparison to the world: 41Electricity - consumption:64.52 billion kWh (2010 est.)country comparison to the world: 39Electricity - exports:0 kWh (2010 est.)country comparison to the world: 120Electricity - imports:0 kWh (2010 est.)country comparison to the world: 123Electricity - installed generating capacity:16.36 million kW (2010 est.)country comparison to the world: 42Electricity - from fossil fuels:66.1% of total installed capacity (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 119Electricity - from nuclear fuels:0% of total installed capacity (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 166Electricity - from hydroelectric plants:21.1% of total installed capacity (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 88Electricity - from other renewable sources:12.8% of total installed capacity (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 17Crude oil - production:26,640 bbl/day (2011 est.)country comparison to the world: 68Crude oil - exports:28,090 bbl/day (2010 est.)country comparison to the world: 51Crude oil - imports:176,000 bbl/day (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 36Crude oil - proved reserves:138.5 million bbl (1 January 2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 69Refined petroleum products - production:181,300 bbl/day (2010 est.)country comparison to the world: 57Refined petroleum products - consumption:315,600 bbl/day (2011 est.)country comparison to the world: 42Refined petroleum products - exports:17,810 bbl/day (2010 est.)country comparison to the world: 74Refined petroleum products - imports:147,900 bbl/day (2010 est.)country comparison to the world: 38Natural gas - production:3.91 billion cu m (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 52Natural gas - consumption:2.86 billion cu m (2010)country comparison to the world: 73Natural gas - exports:0 cu m (2010)country comparison to the world: 167Natural gas - imports:0 cu m (2010)country comparison to the world: 120Natural gas - proved reserves:98.54 billion cu m (1 January 2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 53Carbon dioxide emissions from consumption of energy:85.63 million Mt (2010 est.)country comparison to the world: 41Communications ::PhilippinesTelephones - main lines in use:3.556 million (2011)country comparison to the world: 45Telephones - mobile cellular:94.19 million (2011)country comparison to the world: 14Telephone system:general assessment: good international radiotelephone and submarine cable services; domestic and interisland service adequatedomestic: telecommunications infrastructure includes the following platforms: fixed-line, mobile cellular, cable TV, over-the-air TV, radio and Very Small Aperture Terminal (VSAT), fiber-optic cable, and satellite; mobile-cellular communications now dominate the industryinternational: country code - 63; a series of submarine cables together provide connectivity to Asia, US, the Middle East, and Europe; multiple international gateways (2011)Broadcast media:multiple national private TV and radio networks; multi-channel satellite and cable TV systems available; more than 350 TV stations - 4 major TV networks operating nationwide with 1 being government-owned; some 1100 cable TV providers and some 1,200 radio stations broadcasting; the Philippines is scheduled to complete the switch from analog to digital broadcasting by the end of 2015 (2012)Internet country code:.phInternet hosts:425,812 (2012)country comparison to the world: 52Internet users:8.278 million (2009)country comparison to the world: 34Transportation ::PhilippinesAirports:247 (2013)country comparison to the world: 24Airports - with paved runways:total: 89over 3,047 m: 42,438 to 3,047 m: 81,524 to 2,437 m: 33914 to 1,523 m: 34under 914 m: 10 (2013)Airports - with unpaved runways:total: 1581,524 to 2,437 m: 3914 to 1,523 m: 56under 914 m:99 (2013)Heliports:2 (2013)Pipelines:gas 567 km; oil 138 km; refined products 185 km (2013)Railways:total: 995 kmcountry comparison to the world: 88narrow gauge: 995 km 1.067-m gauge (484 km are in operation) (2010)Roadways:total: 213,151 kmcountry comparison to the world: 23paved: 54,481 kmunpaved: 158,670 km (2009)Waterways:3,219 km (limited to vessels with draft less than 1.5 m) (2011)country comparison to the world: 31Merchant marine:total: 446country comparison to the world: 23by type: bulk carrier 76, cargo 152, carrier 12, chemical tanker 27, container 17, liquefied gas 5, passenger 7, passenger/cargo 65, petroleum tanker 44, refrigerated cargo 20, roll on/roll off 11, vehicle carrier 10foreign-owned: 159 (Bermuda 47, China 4, Denmark 2, Germany 2, Greece 5, Japan 77, Malaysia 1, Netherlands 17, Singapore 1, South Korea 1, Taiwan 1, UAE 1)registered in other countries: 7 (Cyprus 1, Panama 5, unknown 1) (2010)Ports and terminals:Batangas, Cagayan de Oro, Cebu, Davao, Liman, ManilaTransportation - note:the International Maritime Bureau reports the territorial and offshore waters in the South China Sea as high risk for piracy and armed robbery against ships; numerous commercial vessels have been attacked and hijacked both at anchor and while underway; hijacked vessels are often disguised and cargo diverted to ports in East Asia; crews have been murdered or cast adriftMilitary ::PhilippinesMilitary branches:Armed Forces of the Philippines (AFP): Army, Navy (includes Marine Corps), Air Force (2013)Military service age and obligation:17-23 years of age (officers 20-24) for voluntary military service; no conscription; applicants must be single male or female Philippine citizens with either 72 college credit hours (enlisted) or a baccalaureate degree (officers) (2013)Manpower available for military service:males age 16-49: 25,614,135females age 16-49: 25,035,061 (2010 est.)Manpower fit for military service:males age 16-49: 20,142,940females age 16-49: 21,427,792 (2010 est.)Manpower reaching militarily significant age annually:male: 1,060,319female: 1,021,069 (2010 est.)Military expenditures:0.9% of GDP (2005 est.)country comparison to the world: 139Transnational Issues ::PhilippinesDisputes - international:Philippines claims sovereignty over Scarborough Reef (also claimed by China together with Taiwan) and over certain of the Spratly Islands, known locally as the Kalayaan (Freedom) Islands, also claimed by China, Malaysia, Taiwan, and Vietnam; the 2002 ""Declaration on the Conduct of Parties in the South China Sea,"" has eased tensions in the Spratly Islands but falls short of a legally binding ""code of conduct"" desired by several of the disputants; in March 2005, the national oil companies of China, the Philippines, and Vietnam signed a joint accord to conduct marine seismic activities in the Spratly Islands; Philippines retains a dormant claim to Malaysia's Sabah State in northern Borneo based on the Sultanate of Sulu's granting the Philippines Government power of attorney to pursue a sovereignty claim on his behalf; maritime delimitation negotiations continue with PalauRefugees and internally displaced persons:IDPs: at least 843,000 (government troops fighting the Moro Islamic Liberation Front, the Abu Sayyaf Group, and the New People's Army; clan feuds; natural disasters (December 2012 Typhoon Bopha)) (2013)stateless persons: 6,015 (2012)Illicit drugs:domestic methamphetamine production has been a growing problem in recent years despite government crackdowns; major consumer of amphetamines; longstanding marijuana producer mainly in rural areas where Manila's control is limited"
The World Factbook. 2014.
